The Fascinating History of Lego
Introduction
Lego, the beloved toy that has sparked creativity and joy for generations, has a rich and inspiring history. From its humble beginnings in a small Danish workshop to becoming a global phenomenon, Lego’s journey is a testament to innovation, resilience, and the timeless appeal of play.
The Birth of Lego
The Early Years: Ole Kirk Christiansen
 The story of Lego begins in the early 1930s with Ole Kirk Christiansen, a Danish carpenter from the village of Billund. Ole, struggling to make ends meet during the Great Depression, started making wooden toys to supplement his income. In 1932, he founded a small company that would later become known as Lego.
The story of Lego begins in the early 1930s with Ole Kirk Christiansen, a Danish carpenter from the village of Billund. Ole, struggling to make ends meet during the Great Depression, started making wooden toys to supplement his income. In 1932, he founded a small company that would later become known as Lego.
The Name “Lego”
In 1934, Ole Kirk Christiansen decided to name his company “Lego,” derived from the Danish phrase “leg godt,” which means “play well.” Little did he know that this simple name would one day be synonymous with creativity and fun around the world.
The Invention of the Lego Brick
A New Material: Plastic
After World War II, new materials and technologies emerged, including plastic. Ole’s son, Godtfred Kirk Christiansen, saw the potential of plastic for toy manufacturing. In 1947, the company purchased its first injection-molding machine, and in 1949, Lego began producing the first plastic interlocking bricks, initially called “Automatic Binding Bricks.”
The Lego Brick Design
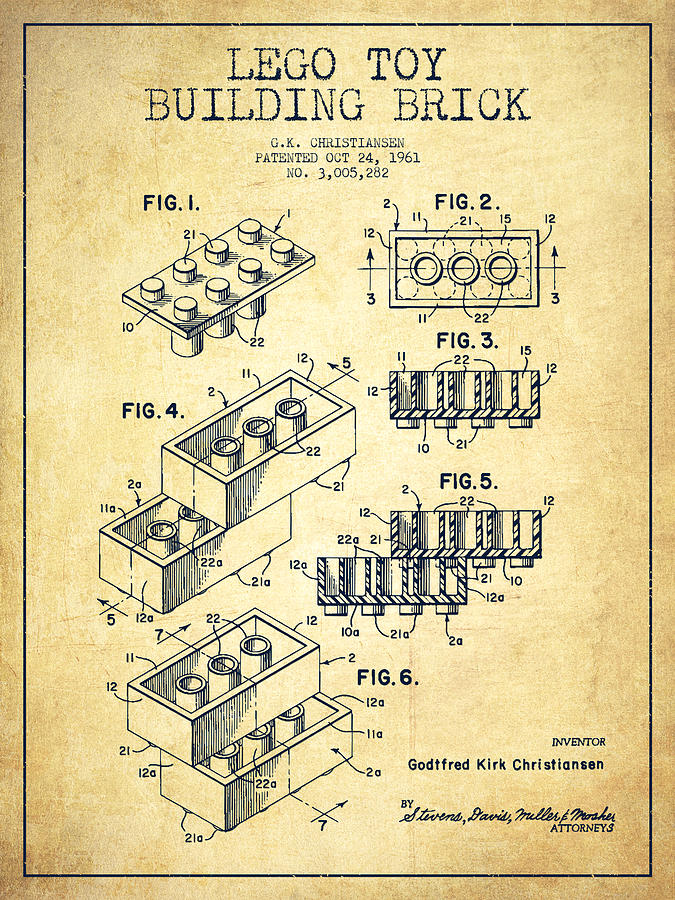
The iconic design of the Lego brick that we know today was patented on January 28, 1958. This new design featured small cylindrical studs on top and tubes underneath, allowing for a snug and secure fit. This innovation was crucial, as it enabled the bricks to interlock firmly and be easily taken apart, providing endless possibilities for construction and creativity.
Growth and Expansion
The Lego System of Play
Godtfred Kirk Christiansen, who took over the company after Ole’s passing in 1958, envisioned a cohesive system of play. He introduced the concept of the “Lego System,” where all pieces were compatible with each other, regardless of the set. This idea revolutionized the toy industry, as it encouraged children to use their imagination to create their own designs, expanding beyond the instructions provided.
The First Themed Sets
In the 1960s, Lego began producing themed sets, starting with town and vehicle sets. This was followed by space, castle, and pirate themes in the 1970s and 1980s. These themed sets not only provided specific building experiences but also inspired children to create their own stories and adventures.
Global Expansion and Innovation
International Presence
Lego’s popularity soared, and by the 1960s, the company started expanding internationally. The first foreign sales office was established in Germany, followed by offices in the United States, Canada, and other countries. Lego’s commitment to quality and creativity resonated with children and parents worldwide, solidifying its status as a global toy brand.
Technic, Mindstorms, and Beyond
In 1977, Lego introduced the Technic line, featuring more complex models with gears, axles, and motors, aimed at older children and teenagers. In 1998, Lego launched the Mindstorms series, combining traditional Lego bricks with programmable elements, paving the way for educational robotics and STEM learning.
Challenges and Resurgence
Financial Struggles
Despite its success, Lego faced significant financial challenges in the early 2000s. Rapid expansion, coupled with a lack of focus and increasing competition from digital entertainment, led to declining profits. The company was at a crossroads, needing to reinvent itself to stay relevant.
A Turnaround
Lego’s resurgence began with a renewed focus on its core product: the brick. Under the leadership of CEO Jørgen Vig Knudstorp, the company streamlined its operations, improved product quality, and invested in understanding its consumers. This strategy paid off, leading to a remarkable turnaround and a new era of growth.
The Modern Era and Cultural Impact
Embracing Digital and Media
In recent years, Lego has successfully integrated digital experiences with physical play. Video games, movies, and TV shows, such as “The Lego Movie,” have expanded the brand’s reach and appeal. Lego also embraces user-generated content and collaborations, fostering a global community of builders.
Educational and Social Contributions
Lego continues to make significant contributions to education and society. The Lego Foundation supports initiatives that promote learning through play, while Lego Education provides resources and tools for educators. Lego also prioritizes sustainability, aiming to produce all core products from sustainable materials by 2030.
Conclusion
The history of Lego is a remarkable journey of innovation, creativity, and resilience. From a small Danish workshop to a global icon, Lego has inspired countless imaginations and brought joy to millions. As Lego continues to evolve and adapt, its commitment to the power of play remains steadfast, ensuring that it will continue to be a beloved part of childhood for generations to come.
